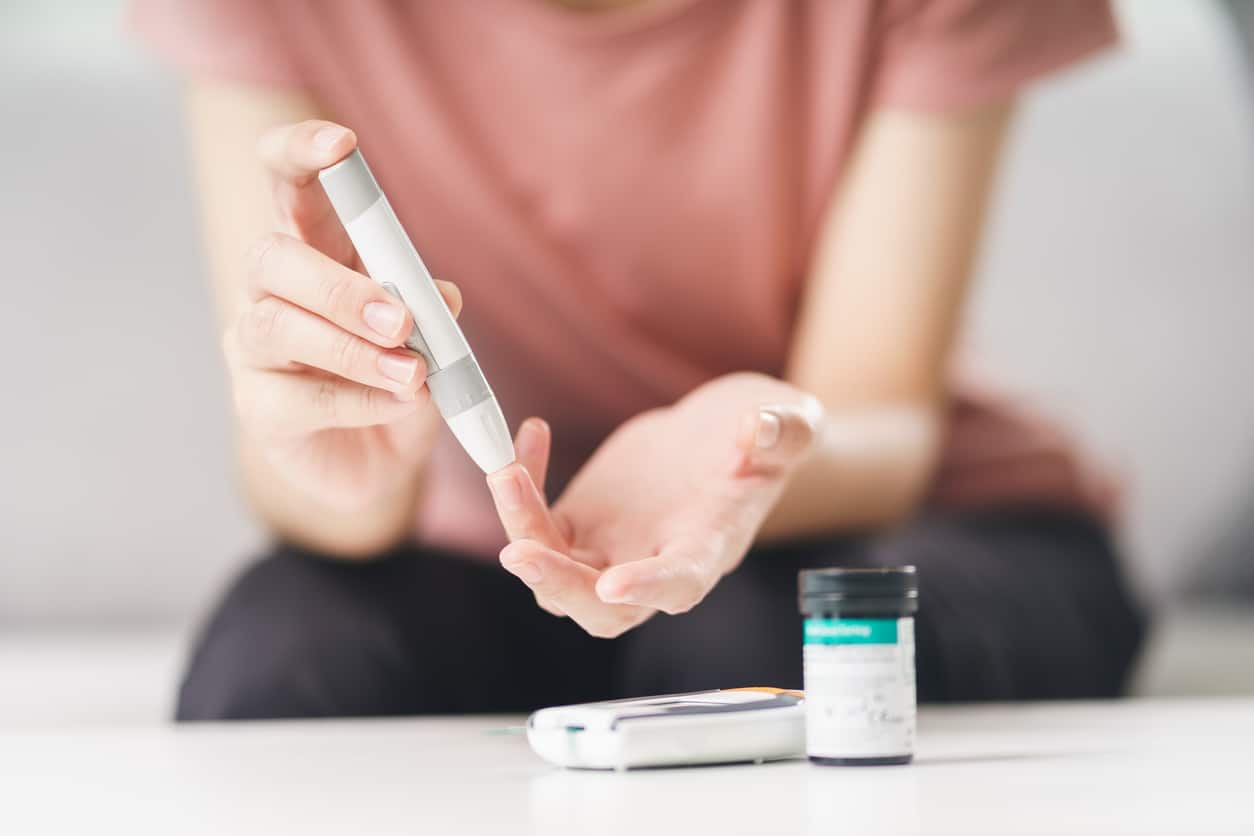
What is diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a condition in which the pancreas is unable to create or use adequate insulin.
Insulin is a hormone created by the body that allows blood sugar to enter cells and be used for energy, and is essential to sustaining life.
There are three distinct types: type 1, type 2, and gestational. There are different symptoms, risk factors, and treatment plans depending on the type of diabetes. These are explored in more detail below.
Type 1
When someone has type 1, it means that their immune system attacks and destroys the pancreas’ ability to create insulin. This type is the least common.
Symptoms
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes generally begin early in life, and the typical symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Dry skin
- Extreme thirst
- Increased hunger
- Frequent urination
- Blurry vision
- Wounds that are slow to heal
- Numbness or tingling in extremities
- Abnormal number of infections
Diagnosis
If a provider suspects a person has type 1 diabetes, they will administer a Random Plasma Glucose (RPG) test which measures blood glucose level.
People with type 1 are usually diagnosed at an early age, with most diagnoses being discovered around 13-14 years of age. However, people can be diagnosed at earlier ages or even later ages.
Risk Factors
The largest risk for type 1 is a family history of the condition. Additionally, frequent infections and viruses can increase the risk for this type.
Type 2
Type 2 diabetes is developed, although you can be predisposed to the condition if it runs in your family. This condition is caused by the pancreas being unable to control blood sugar levels with insulin and leads to the body producing more insulin until it is unable to keep up with the demanded amount.
Symptoms
People with diabetes- especially type 2- may not have any symptoms of the condition at all. However, if you notice any of the above symptoms, it may be time to visit your primary care provider and get tested.
Diagnosis
Type 2 is diagnosed by using blood sugar tests. These tests are usually done routinely at annual physicals or check-ups at primary care providers. At MainStreet Family Care, we offer blood sugar tests and annual physicals in our primary care services.
Risk Factors
People who live unhealthy lifestyles are the most at risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Risk factors that can lead to type 2 diabetes include:
- Being overweight or obese
- Smoking or using tobacco
- Eating an unbalanced or unhealthy diet
- Having the condition in your family history
- Not having an exercise routine
- Those who are 45 years old and older
- Having pre-diabetes
- Previously had gestational diabetes
Complications
Those diagnosed with type 2 diabetes are also at a higher risk for developing other health problems and complications. These conditions include:
- Heart attack, stroke, heart disease, and heart failure
- Partial and total vision loss, as well as eye diseases
- Kidney failure and kidney disease
- Diabetic neuropathy
- High cholesterol
Gestational
Gestational diabetes is developed by pregnant women and generally only lasts until the baby is born. Although the condition resolves itself post-pregnancy, women who have gestational diabetes are more at risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Additionally, this is most common in women over 25 years of age.
Pre-diabetes
Pre-diabetes is a condition in which a person’s blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not yet in the range of being diabetic. If you are diagnosed with this condition, you should be hypervigilant about monitoring your sugar levels as well as changing your lifestyle in order to lower your levels.
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is different from diabetes in that your body doesn’t respond well to insulin, causing your pancreas to create more insulin than what is really needed. This condition can lead to diabetes.
What Are The Treatment Options?
Diabetes is a chronic condition, meaning that it cannot be cured. People with diabetes are usually prescribed insulin, which can be taken in several different ways. Common forms of insulin include:
- Inhaler
- Syringe and needle
- Jet injector
- Insulin pump
- Pen
- Artificial pancreas
In cases of type 2, you can treat your condition by making lifestyle changes. Some of the best lifestyle changes to manage diabetes include:
- Losing weight
- Changing your diet
- Developing an exercise routine
- Being more active in your daily life
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Stop smoking or using tobacco products
- Receive frequent physicals or checkups
Turn To MainStreet Family Care
MainStreet Family Care can help you heal and feel better, fast! Our primary care providers see patients seven days a week, and we offer same-day and next-day appointments.
Visit the patient portal to sign up for an account and make your first appointment.